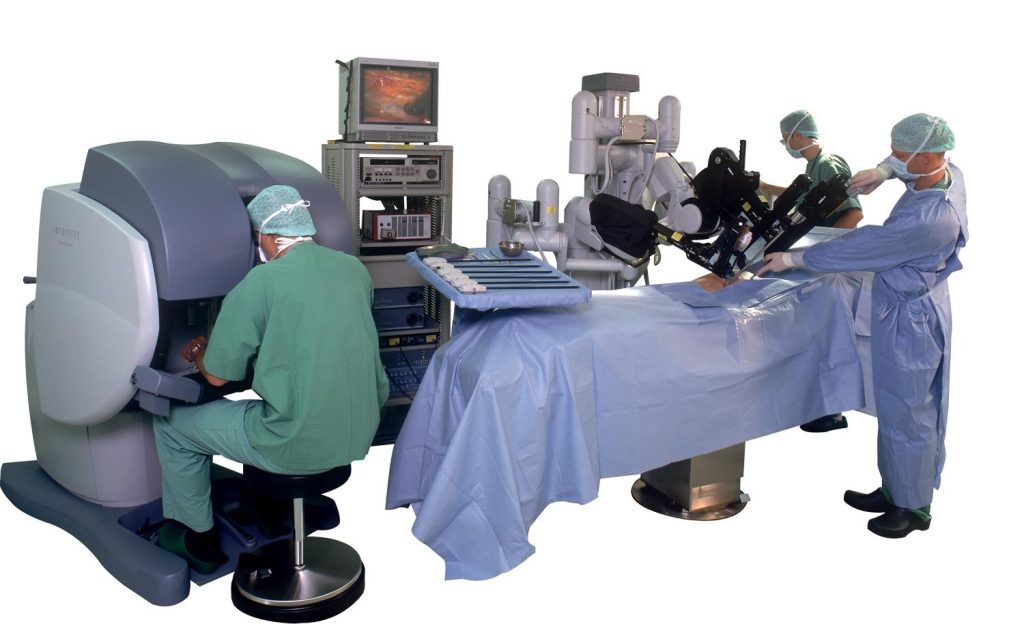
What is robot-assisted surgery?
Robot-assisted surgery is a type of minimally-invasive surgery completed through small incisions. The da Vinci surgical system uses high-definition, three-dimensional cameras that magnifies image 20 times coupled with specialized surgical tools that enable surgeons to operate with more precision and better control.
The robotic instruments have mechanical wrists that bend and rotate to mimic the movements of the human wrist thus allowing surgeons to make precise movements. Robotic software also negates the effect of surgeons’ hand tremors.
It is an effective minimally invasive alternative to both open surgery and laparoscopy. Surgeons undergo vigorous training with this system before being allowed to use it for surgery on patients. Moreover, there are many inbuilt safety checks in the system that decreases the chances of error. Patients can be rest assured knowing they’ll receive superior surgical care for the best possible outcome.
How robot-assisted surgery works ?
During robotic surgery, your surgeon inserts a tiny camera through a small incision in the surgical area. The camera sends a high-definition, 20 times magnified, 3D image of the surgical site to an external monitor in real-time.
Using computer-assisted technology that guides specialized surgical instruments, your surgeon directs the robot with better control, precision, and range of motion than is possible with traditional surgery. A support team assists the surgeon with other surgical tasks. Thus the use of a robotic system makes difficult steps easier for the surgeon by providing a range of motion and more maneuverability in handling tissue and suturing.
Will the surgeon be with me in the operating room?
Many patients wonder who is operating on them: the robot or the surgeon.
Robot-assisted surgery is a system that enables surgeons to operate with precise, delicate motions by controlling the machine. The robot never makes decisions or performs incisions on its own — it only responds to your surgeon’s hand and finger movements.
Your surgeon is located at a console in the operating room near you and the experienced support staff, directing the procedure the entire time. The robot allows for greater precision than the human hand has on its own, and your surgeon is in charge the whole time.
Conditions that can be treated with robot-assisted surgery
The majority of gastrointestinal issues can be addressed using robotic-assisted minimally invasive surgery, including:
- Appendicitis
- Hernias
- Gallbladder disease and its cancer surgery
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Liver surgery
- Surgery of the pancreas including surgery for cancer of the pancreas
- Surgery for the colon and rectum including its cancers
- Surgery for the esophagus, stomach, and intestine
- Gastrointestinal and liver cancer surgery.
The benefits of robotic surgery
Robot-assisted surgery has many benefits. Patients experience these benefits both directly and indirectly. For example, because robot-assisted surgery is minimally invasive, a direct benefit to you is a shorter recovery time. And because the surgeon has better access to the operative area, an indirect benefit is a more precise surgery.
Other benefits include:
- Smaller incisions
- Greater range of motion and dexterity for the surgeon
- High-resolution, the highly-magnified image of the operating field for better visualization during surgery
- Shorter hospital stay
- Lower risk of infection
- Reduced risk of blood loss
- Faster recovery with less pain
- Minimal scarring
- Better clinical outcomes
In addition, due to the enhanced control, flexibility, and precision that robot-assisted surgery offers, surgeons can complete complex or delicate procedures that may be difficult or impossible with traditional surgery.
Am I a candidate for robot-assisted surgery?
Although robotic surgery offers excellent outcomes for many patients, not everyone is a good candidate. The patient is recommended against robot-assisted surgery if:
- You’re unable to have general anesthesia
- You have significant scar tissue or other issues that prevent the cameras from visualizing the surgical area
- You’ve been diagnosed with bleeding problems that put you at risk for surgery
- You’re not a candidate for laparoscopic surgery
After a full evaluation of your condition and overall health, the surgical team in charge will determine if robot-assisted surgery is right for you.
What Are the Advantages of Robotic Surgery Over Laparoscopic Surgery
Robotic surgery is a minimally invasive surgical technique that uses a robotic arm to perform surgery.
The robotic arm is controlled by the surgeon, who sits at a console and uses a joystick to manipulate the arm. This allows the surgeon to perform surgery with greater precision and dexterity than is possible with laparoscopic surgery.
If you are considering robotic surgery, here are some things you can expect:
- You will be given general anesthesia, which will put you to sleep during the surgery.
- The surgeon will make a small incision in your abdomen and insert the robotic arm.
- The surgeon will then use the robotic arm to perform the surgery.
- The surgery will typically take less time than traditional open surgery.
You will likely be able to go home the same day or the next day after the surgery.
Overall, robotic surgery is a minimally invasive surgical technique that offers several advantages over laparoscopic surgery. If you are considering surgery, talk to your doctor about whether robotic surgery is a good option for you.
Advantages of Robotic Surgery
Here are some of the specific advantages of robotic surgery over laparoscopic surgery:
- Improved visualization: Robotic surgery provides the surgeon with a magnified, 3D view of the surgical site. This allows the surgeon to see more clearly and make more precise movements.
- Greater dexterity: The robotic arm has a greater range of motion than the human hand. This allows the surgeon to reach areas that would be difficult or impossible to access with laparoscopic surgery.
- Tremor-free movements: The robotic arm is tremor-free. This means that the surgeon can make very precise movements without the risk of shaking.
As a result of these advantages, robotic surgery has been shown to have several benefits over laparoscopic surgery, including:
- Less pain: Robotic surgery is associated with less pain and a shorter recovery time.
- Lower risk of complications: Robotic surgery is associated with a lower risk of complications.
- Better cosmetic outcome: Robotic surgery is associated with a better cosmetic outcome.
However, it is important to note that robotic surgery is not always the best option for every patient. Some patients may be better suited for laparoscopic surgery or traditional open surgery. It is important to discuss your options with your doctor to determine which type of surgery is right for you.

 Book An Appointment
Book An Appointment