Best Bariatric Surgeon in Chandigarh
Dr. MS Bedi being the best Bariatric and Metabolic Surgeon in Chandigarh, Mohali, and Panchkula can ably handle all kinds of Weight Loss/Bariatric Surgery Procedures and their complications. Considering his expertise, he can handle cancerous and noncancerous conditions even in advanced stages.
Bariatric Surgery in Chandigarh
Obesity is a huge issue not only in developed nations but also in developing nations like India. It has affected 5% of the country’s population.
For severely obese patients, if the non-surgical treatments fail, weight loss surgery or bariatric surgery may be the only option.
Why it’s done
Bariatric surgery helps patients lose pounds and maintain a healthy weight by restricting calorie intake and causing malabsorption. The various types of bariatric surgery procedures that may be recommended that uses different techniques to help the patients.
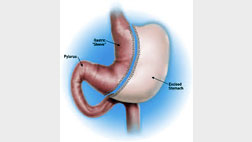
Commonly done procedures in Bariatric Surgery
- Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy
- Laparoscopic Mini Gastric bypass
- Laparoscopic Roux-Y Bypass
- Laparoscopic sleeve with duodenojejunal bypass
Bariatric Surgery Cost in Chandigarh
To know more about the Bariatric Surgery, Weight Loss Surgery, treatment and cost estimate for operation, please share your request and reports at [email protected].
Indication of Bariatric Surgery
- BMI of 32.5 with any of obesity related diseases – Diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnoea, PCOD etc.
- BMI of 35 or more
- Uncontrolled diabetes in obese patients.
- BMI (Basal Metabolic rate) = Weight(kgs)/Height(m)2

Frequently Asked Questions about Bariatric And Metabolic Surgery
| BMI | Status 1 |
|---|---|
| 18.5 – 24.9 | Normal |
| 25 – 29.9 | Overweight |
| 30 – 34.9 | Obese |
| 35 – 39.9 | Severe Obesity |
| >40 | Morbid Obesity |
| > 50 | Super morbid Obesity |
* Among Asian Indians, the recommended BMI for obesity surgery is >32.5 with co=morbid illnesses and >37.5 in Obese individuals. (Consensus Statement for diagnosis and treatment of Obesity, JAPI, Vol.57, February 2009. www.japi.org)
National Institutes of Health and National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Clinical guidelines on the identification, evaluation, and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults—the evidence report. Obes Res 1998;6(suppl 2):1S-209S.
| Co-Morbidity | Percentage of more risk |
|---|---|
| Diabetes | 20-40% |
| Hypertension | 25-55% |
| Hyperlipidemia | 35-53% |
| Cardiac disease | 15-25% |
| >Respiratory disease | 10-20% |
| >Sleep apnea | 20-30% |
| >Arthritis | 20-30% |
| >Depression | 70-90% |
| >Stress Incontinence | 40-50% |
| >Menstrual irregularity | 15-25% |
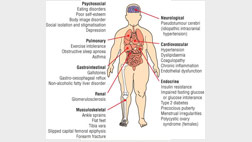
With BMI > 30 there is 55% increase in mortality, 70% increase in coronary artery disease, 75% increase in stroke and 40% increase in diabetes. So, morbidly obese males between 25 and 35 have 12x the chance of dying as normal-weight men. A morbidly obese adult has a 33% less chance of living to age 65 than that a normal-weight person.
That is the reason why surgery for obesity has great relevance in treating excess weight and curing/improving most of these medical conditions along with the surgery.
This procedure results in an overall reduction in body weight and helps to improve associated medical disorders of excess body weight. Liposuction is a cosmetic surgery wherein part of body fat is removed using high-power suction, which usually does not produce any sustained weight loss.
Awareness about the type of food you should eat can help you in planning a wholesome diet that is adequate in an amount that won’t allow you to feel hungry and still you would lose weight. Dieting does not mean eating less but it should be eating right and it is a lifelong commitment. Short-term dieting results in failure and loss of morale.
Because 3,500 calories equals about 0.45 kilogram of fat, you need to burn 3,500 calories more than you take in to lose .045 Kg. So one need to plan out caloric intake and do regular exercises to have good weight loss. Here is a chart to have an idea about how much weight loss you can achieve with diet and exercises.
| Activity (1-hour duration) | Weight of person and calories burned | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 70 kilograms | 90 kilograms | 100 kilograms | |
| Aerobics, high impact | 533 | 664 | 796 |
| Aerobics, low impact | 365 | 455 | 545 |
| Aerobics, water | 402 | 501 | 600 |
| Bicycling, < 10 mph, leisure | 292 | 364 | 436 |
| Running, 5 mph | 606 | 755 | 905 |
| Running, 8 mph | 861 | 1,074 | 1,286 |
| Stair treadmill | 657 | 819 | 981 |
| Swimming | 423 | 528 | 632 |
| Walking, 2 mph | 204 | 255 | 305 |
| Walking, 3.5 mph | 314 | 391 | 469 |
Along with weight loss, most of the medical co-morbidities improve which in turn improves patients’ self-esteem and confidence. Some of the important benefits are Diabetes mellitus Type II in these patients improves and a vast majority of them become completely normal blood sugar levels normal after surgery. Hypertension & high cholesterol improves significantly. These effects along with a good amount of weight loss reduce the risk for heart disease significantly.
There is a good relief for sleep problems, apnoea, and acid reflux symptoms. As the body weight comes down body pain and joint arthritis improve very well. Overall improvement in the sense of well-being and self-esteem.
The effect of these procedures is long-term in terms of weight loss and improvement of co-morbidities if the patient adheres to the follow-up advice of the doctor.
- Sleeve Gastrectomy: In this procedure stomach is converted to a long tube-like structure to reduce its capacity. This is less complex operation and produces about 65-75% of excess weight loss.
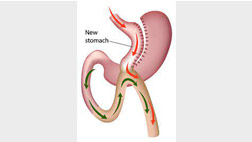
- Mini Gaastri bypass – in this procedure stomach is converted from pouch like shape to tube like structure and small intestine is joined to it so that food bypass large amount of small intestine where food is absorbed thus resulting in lesser absorption of food. This procedure result in around 70- 85% of excess weight loss.
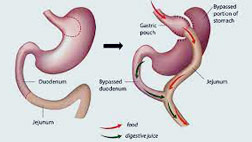
- Roux-en-Gastric Bypass (RYGB) procedure: Here the stomach is stapled to convert it to a small pouch and this helps in restricting food intake. Further a segment of intestine is bypassed from the food stream so that nutrients are exposed to less absorptive surface of small intestine. So this is a restrictive and malabsorptive procedure, which results in 70-85% of excess weight-loss.
- Sleeve gastrectomy with duodenojejunal bypass – Here stomach is converted from pouch like shape to tube like structure and distal small intestine is anastomosed to duodenum thus bypassing large amount of absorptive area of small intestine. This procedure although slightly complex but has lesser side effect.
Skin does have some elasticity to it and will recoil or bounce back when weight is lost. However, when a large amount of weight is lost in a short period it is much more difficult for all the skin to bounce back so that there is no excess. This is when the patient must consider the option of plastic surgery to remove this excess skin.

 Book An Appointment
Book An Appointment